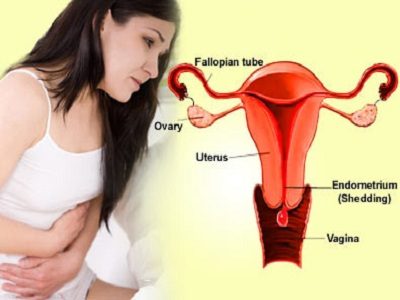
Heavy Bleeding
Whats heavy bleeding
Excessive menstrual bleeding affects one in five women. This leaflet describes some of the problems women experience with heavy bleeding, and suggests ways of coping. It explains the treatments which your doctor or gynecologist is likely to offer, and also mentions complementary therapies. The leaflet aims to help women make informed decisions about the treatment choices for heavy bleeding.
The amount of blood lost in each period varies enormously from individual to individual. Some women lose a few teaspoonfuls and hardly notice their periods, while other women regularly lose large volumes of blood. Because of this wide variation it is impossible to define a ‘normal’ period in terms of the amount, length, and frequency of bleeding. A heavy period for one woman may be normal for another.
-
However, for any individual woman, the amount of blood lost every month tends to remain relatively constant, apart from slight variations with age. It would be unusual for a woman to lose a few teaspoonfuls of blood one month and a pint of blood the next. Because the amount of blood loss is relatively constant, each individual woman tends to consider her own periods to be normal for her, and usually only worries about them or consults her doctor when she feels that her periods have changed.
-
Doctors define menstrual bleeding as heavy (and call it menorrhagia) when periods last longer than seven days or more than 80ml of blood is lost during a period. It is possible to measure menstrual blood loss and doctors can have this done by their local hospital departments, especially if there is concern about a woman becoming anaemic. However, the way that a woman perceives the heaviness of her period is as important as any clinical measurements.
Clots
-
When menstrual bleeding is heavy, clotting can also occur. Losing large clots can be extremely upsetting and even painful if they are large because they can cause cramping as they pass through the cervix. There is a simple explanation as to why these large clots are formed. All blood contains a clotting factor. To enable menstrual blood to flow freely from the uterus (womb) and leave your body without clotting, the uterus produces an anti-clotting agent. But if the menstrual loss is heavy, it is possible that the anti-clotting agent will be used up before a period has finished, so that the remaining blood is likely to form clots.
Whats causes heavy bleeding ?
- If your periods have changed, it’s very important to see your doctor. There are a number of diseases which can cause heavy bleeding (see list below). The doctor will investigate possible causes and offer the appropriate treatment. But in about half the women with heavy bleeding, no cause can be found.
- Some causes of heavy menstrual bleeding.
- If your periods have changed, it’s very important to see your doctor. There are a number of diseases which can cause heavy bleeding (see list below). The doctor will investigate possible causes and offer the appropriate treatment. But in about half the women with heavy bleeding, no cause can be found.
- Unexplained – for half of all cases no cause can be found
- Contraceptive coil (IUD) – the coil can cause heavier, longer periods.
- Injectable contraception (Depo Provera) – can cause heavy or prolonged bleeding.
- Pelvic disorders:
- Fibroids – these benign (not cancerous) growths in the muscular wall of the uterus are a common cause of heavy bleeding
- Polyps – these benign growths of the lining of the uterus may cause heavy bleeding but more commonly lead to spotting between or after periods.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease – an infection in the reproductive tract which can cause infertility and chronic pain if untreated.
- Endometriosis – a painful condition in which the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus.
- Endometrial hyperplasia – thickening of the lining of the uterus, leading to heavier bleeding.
- Endometrial cancer – cancer of the lining of the uterus, causing heavy periods, bleeding between periods and blood-stained vaginal discharge. Rare, but more common in women after the menopause.
- Blood and hormonal conditions:
- Hormone imbalances – can stop ovulation (egg release) leading to build-up of endometrium and heavier periods.
- Hypothyroidism – an underactive thyroid gland can cause heavier periods.
- Blood clotting disorders.
- Use of anticoagulant drugs.
10 Minute Solution to Heavy Bleeding
- Lakhs of women in India suffer from the problem of heavy bleeding during their periods. This not only causes extreme inconvenience, discomfort, loss of work days and exclusion from religious activities but also severe weakness and anaemia.
- Many of these women in their 30’s and 40’s are suffering from dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB) where the womb (Uterus) is normal, yet they have heavy menses. The diagnosis of DUB is made by an internal examination by the gynaecologist. A sonography will confirm that there are no tumours, which are causing the heavy bleeding or cancers and she is a case of DUB. Over the years these women have been treated with prolonged hormonal treatment, repeated curetting or removal of the womb by a major surgery (hysterectomy) all of which have significant risks and complications.
- Two new techniques have made the management of heavy menses simple, safe and quick.
- The uterine balloon ablation therapy involves putting a small tube with an inflatable balloon at the top, into the womb through the vagina. There are no cuts or stitches required for this. The balloon is filled with hot water through a computerized machine and the lining of the womb is heated for 8 minutes. This thins the lining of the womb and prevents it from growing. This procedure can be done under local or general anaesthesia and can be safely done even in patients who have medical problems such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart or kidney disease where other operations are risky to perform. This results either in stoppage or reduction in menstrual bleeding permanently. Hence this procedure is good for women who have completed their family. The patient needs to be in hospital only for a few hours and is fit to resume work from the next day,
- The other simple, non surgical method of treating heavy menses is to insert a hormonal intrauterine device (LNG _ IUD). This is a small shaped ‘T’device, which looks like a Copper T or loop but has hormone inside it. This can be placed inside the uterus in two minutes, without any anaesthesia and once inside the womb, it reduces or stops bleeding during menses for a period of 5 years. This also gives contraceptive benefit to women . This is a temporary method and the device can be removed at any time. Both these methods are simple and safe and give good results in well selected patients.
FAQ
Q.1. I am 42 years old and have regular but very heavy menses with clots. My sonography is normal and I have been taking hormones on and off for this problem. I am fed up as I cannot even go to work with such heavy bleeding and am worried about the side effects of hormonal treatment.
Ans: If you have finished your family there are many options for you. You can insert a hormone loop or intrauterine device which can be kept inside the womb for 5 years and it reduces or stops bleeding in most patients. Another technique which is quite simple and safe is uterine balloon ablation, in which a tube with a balloon at its end is put into the womb. Hot water is circulated through it, which causes the lining of the womb to be damaged and so bleeding permanently stops. There is also the option of hysterectomy or removal of the womb which can be done vaginally or through key hole (laparoscopic) surgery or by giving a small bikini scar. This will permanently stop bleeding and there will be no risk of cancer of the womb in the future